 Places
Places
 Middle East
Middle East
 Israel
Israel
 Israel - Palestine - History
Israel - Palestine - History
Don's Home
 Places
Places
 Middle East
Middle East
 Israel
Israel
 Israel - Palestine - History
Israel - Palestine - History
| Contact |
| Palestine History | Israel | Israel Politics | Arab Israeli Wars | 2023 Israel Hamas War" | Antisemitism | Hate Crimes | | Bias in Arab-Israeli Conflict |
Contents: Intro | Brief History | Jewish History | Palestine History | Population: Historical Current
Click on Images to get source documents
Intro:
I started this page after October 7, 2023 when Hamas, the Iran-backed terror group controlling Gaza launched an unprovoked and vicious surprise attack on over 20 communities in Israel and Israel responded with a war to destroy Hamas.
I wanted to look at the history of Palestine over the last 4 millenia (4,000 years) and how it got to this point.
Note I am using Palestine loosely it is generaly considered the area between the Mediterranean Sea and Jordan River, but after WW I it included area all the way to Iraq.
 1060 CE Sykes
Brief Summary of who does Israel/Palestine belong too, then and now that the Romans and other conquering empires are gone:
1060 CE Sykes
Brief Summary of who does Israel/Palestine belong too, then and now that the Romans and other conquering empires are gone:
Note: I'm using the old term BC for the period before Christ, know known as BCE Before Common Era, but CE (Common Era) for the time which was called AD (anno Domini). We are now in the 21st century CE.
The word Palestine derives from ancient Greek (Philistia), but ancient Egyptian, Assyrian and Hebrew languages also included similar-sounding words to describe the region or its people.
Following the 1918 fall of the Ottoman Empire during World War I, Palestine typically referred to the region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. Much of this land is now part of present-day Israel.
According to History.com, More than 135 United Nations member countries recognize Palestine as an independent state, but Israel and some other countries, including the United States, don't make this distinction.
Palestine's status in the UN (2023) is a "non-member state". not a Nation.
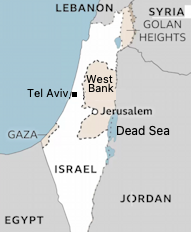
It is defined by the Gaza strip and the West Bank. The Golan Heights, also captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War, is considered to be Syrian territory held by Israel under military occupation.
The CIA World Factbook breakes it up into 3 regions Israel, West Bank and Gaza Strip.
Strategically situated between three continents, the region of Palestine (also known as the Land of Israel and the Holy Land) has a tumultuous history as a crossroads for religion, culture, commerce, and politics. Palestine is the birthplace of Judaism and Christianity, and has been controlled by many kingdoms and powers, including Ancient Egypt, Ancient Israel and Judah, the Persian Empire, Alexander the Great and his successors, the Hasmoneans, the Roman Empire, several Muslim caliphates, and the crusaders. In modern times, the area was ruled by the Ottoman Empire, then the British Empire
Status of Israel and Palestine in the United Nations:
Israel is currently a country recognized by the United Nations since 1948. Palestine is a Nation State.
As of June 2024, the State of Palestine is recognized as a sovereign state by 144 of the 193 member states of the United Nations. It has been a non-member observer state of the United Nations General Assembly since November 2012.
The State of Palestine had been officially declared by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) on 15 November 1988, claiming sovereignty over the internationally recognized Palestinian territories: the West Bank, which includes East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip.
538
The British, who held a colonial mandate for Palestine until May 1948, opposed both the creation of a Jewish state and an Arab state in Palestine as well as unlimited immigration of Jewish refugees to the region. Great Britain wanted to preserve good relations with the Arabs to protect its vital political and economic interests in Palestine..
On November 29, 1947 the United Nations adopted Resolution 181 (also known as the Partition Resolution) that would divide Great Britain’s former Palestinian mandate into Jewish and Arab states in May 1948 when the British mandate was scheduled to end. Under the resolution, the area of religious significance surrounding Jerusalem would remain a corpus separatum under international control administered by the United Nations.
On May 14, 1948, David Ben-Gurion, the head of the Jewish Agency, proclaimed the establishment of the State of Israel. U.S. President Harry S. Truman recognized the new nation on the same day.
In 2024 the UN Security Council blocked Palestine’s bid to become a full member of the United Nations due to a United States veto on a draft resolution that would have recommended the granting of such status.
The proposal, submitted by Algeria, received 12 votes in favour, with the United States casting a negative vote and Switzerland and the United Kingdom abstaining.
As of June 2024 Among the G20, nine countries (Argentina, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, and Spain have recognized Palestine as a state,[note 1] while ten countries (Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Mexico, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and the United States) have not.[note 2] Although these countries generally support some form of a two-state solution to the conflict, they take the position that their recognition of a Palestinian state is conditioned to direct negotiations between Israel and the PA.
Another issue is there is no central government. The Palestinian Authority was created to exert partial civil control in the West Bank enclaves and in the Gaza Strip. The Gaza Strip is de facto under the administration of the Hamas government since 2007.
See International recognition of the State of Palestine | Wikipeda
- 2000 BC God God promises Abraham, the founder of the Jewish people, who lived in Ur near today's Baghdad , the land of Cannan (Promised Land), which is where modern Israel is today.
- 1800 BC - The 12 sons of Jacob (also known as Israel) represent 12 tribes who collectively form the Israelite nation.
Israeli Patriarchs: Jacob is the son of Issac, Issac is the son of Abraham.
- 1446 BC Moses leads them out of Egypt.
- 1400 BC Joshua takes Jericho from the Canaanites
- 1200 BC Deborah defeats Canaan (There is historical evidence for this)
Current scholarly research has shown that much of what is in the bible is myth.
However, the story of the Egyptian captivity and Exodus has done much to unify Jews.
Current genetic and archeological studies show that the origins of the Jewish people are multifaceted and cannot be attributed to a single source or location.
Current thinking is the Jewish people are believed to have descended from ancient Canaanite tribes that inhabited the Levant region (Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine/Israel, Syria, Turkey), which includes present-day Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and the Palestinian territories.
Whether the United Monarchy of Israel existed - and, if so, to what extent - is a matter of ongoing academic debate, and scholars remain divided between those who support the historicity of the biblical narrative, those who doubt or dismiss it.
Isreal - united monarchy | Wikipedia
Prior to the establishment of a kingdom, came the period of the Judges. Israel was a theocracy with Judges determining the will of God.
When the Judge Samuel grew old, he appointed his sons as judges for Israel, people rejected them saying "did not walk in his ways." and wanted a king like all the nations.
1047 BCE–930 BCE - United - Split Israel: David, Solomon
Israel united-split
The United Monarchy | Associates for Bible Research
1037 - 1050 BC Samuel
appointes Saul then David as Kings in the transition to a monarachy.
David greatly expanded the kingdom's borders and conquered Jerusalem from the Jebusites, turning it into the national, political and religious capital of the kingdom.
David's son Solomon takes over, but has issues.
930 BC The Kingdom of Israel split into two kingdoms the Northern Kingdom of Israel and the southern Kingdom of Judah after the reign of Solomon.
There were several reasons, taxes, geography, ... . See the Israel page.
The tribes of Judah and Benjamin composed the South (Judah) wich contained the capital Jerusalem on the border.
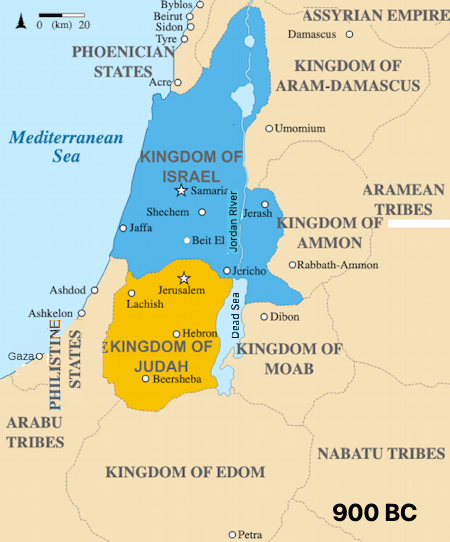
The remaining ten tribes controlled the North (Israel).
Israel and Judah, controlled much of Palestine, while the Philistines occupied its southern coast.
722 BC, the 10 tribes of northern Israel were conquered by the ancient Assyrian Empire.
597 BCE Babylonian conquest. The Babylonian exile, or Babylonian captivity, was the deportation of the Jews (mostly elite) of the ancient Kingdom of Judah to Babylon by Nebuchadrezzar II. Some also fled to Egypt.
The exile occurred after the defeat of the Jews in the Jewish-Babylonian War and the destruction of Solomon's Temple.
559 BC Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid (Persian) Empire conquered the Babylonians and freed the Jews. it made the re-establishment of the city of Jerusalem and the rebuilding of the Temple possible
330 BC - Alexander the Great, king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon.
the Greeks believed that God existed, which is very important because it will help explain one reason why Alexander was able to tolerate the Jewish religion, whereas many of the Persian emperors were not.
301 BC - Jews Ruled by Ptolemies (A Egyptian dynasty with Greek rulers)(301 BCE)
215-163 BC Hellenistic Seleucid Empire Led by Greek Antiochus IV Epiphanes they expanded to Egypt and Middle East.
167 BC - The continuing Hellenisation of Palestine led to the Maccabean revolt.
Judas Maccabeus, Israeli priest, defeated them.
Festival of Hanukkah established in honor of the capture of Jerusalem
63 BC-450 CE Roman Empire
1st Century CE
66-73 CE First Jewish Revolt, Jerusalem destroyed
Rome destroyed the Second Temple and forbade Jews to live in the remaining parts of Jerusalem;
A Jewish diaspora (Exile) existed for several centuries before the fall of the Second Temple, and their dwelling in other countries for the most part was not a result of compulsory dislocation
1st century CE - Christians claimed Jesus was the Jewish Messiah and that Christianity was the true Judaism
115-117 CE Annihilation of Jews in Egypt. Jews are blamed for what was mostly a Roman domination of Egypt.
132-135 CE Second Jewish Revolt
Romans responded by expelling most Jews from Judea. This expulsion marked the beginning of the Jewish diaspora, or the dispersion of Jews around the world.
587 - Babylonian exile
613 - Persian-Jewish forces captured Caesarea and Jerusalem, destroying its churches, massacring its Christian population,
40's and 50's CE St. Paul's, Barnabas and Stephen's Christian missionary journeys concentrated on Gentiles, while other apostles, e.g. Peter, James the Just and John, concentrated on converting Jews. They were all successful.
Some Christions claimed that Jesus was the messiah.
315 CE Sometime prior to the Council of Nicaea, Emperor Constantine declares Christianity (Catholicism) the official religan of the Roman Empire.
395 CE - The split of the Roman Empire This area became known as the Byzantine Empire, due to the the imperial seat of the Roman Empire moving from Rome to Byzantium.
5th Century CE - Christianity is the dominant religion of most of Palestine
415 - Expulsion of Jews from Egypt
Christian monks often led attacks on synagogues during the Holy Week of Easter.
632-661 Arab leader Muhammad founded a new monotheistic religion called Islam. His followers became known as Muslims. Muhammad united the Arabian tribes into a religious polity, a caliphate,CE Muslim armies attacked and occupied parts of north Africa, Israel/Palestine, and parts of the middle east (including what we today call Lebanon, Syria, Iran, and Iraq.)
Palestine comes under Muslim control.
Muselams built the Dome of the Rock on the Temple Mount in the Old CIty of Jerusalem.
1096-1300 CE High Middle Ages - Crusades were, in essence, military expeditions initiated by the medieval papacy to wrest the Holy Lands from Muslim control.
1095-1101 First Crusade - Capture of Antiochus and Jerusalem by the Christian crusaders. 12-30,000 men
500-1500 CE - Middle Ages - Jews were restricted from many occupations. An exception was money lending, often stemming from restrictions imposed by Christian religious doctrine.
But later many were restricted from money lending (usery - lending money for interest).
1453-1566 - The land which would become Israel was for centuries part of the Turkish-ruled Ottoman Empire.
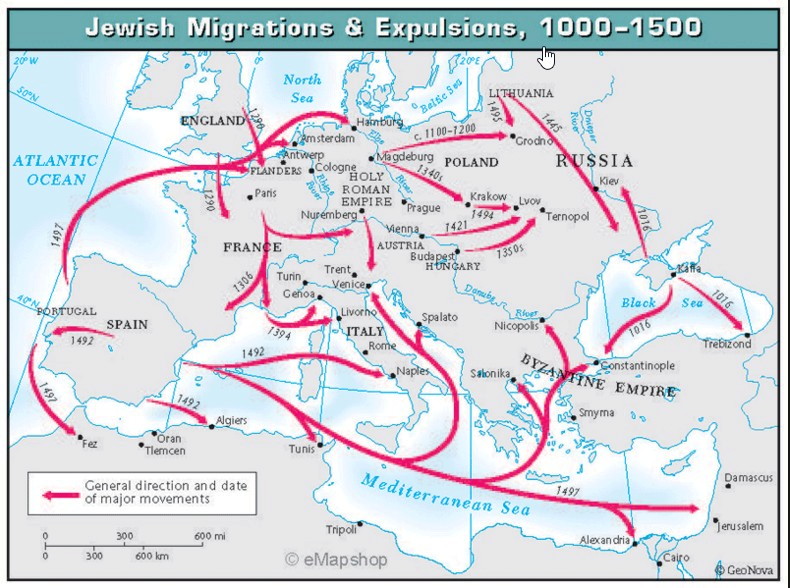
Middle Ages 19th century - The rise of Zionism, started in Europe seeking to recreate a Jewish state in Palestine
1881-1903 The First Aliyah (Jewish Immigration), also known as the agriculture Aliyah, was a major wave of Jewish immigration (aliyah) to Ottoman Syria between 1881 and 1903. Jews who migrated in this wave came mostly from Eastern Europe and from Yemen. An estimated 25,000 Jews immigrated. Many of the European Jewish immigrants during the late 19th-early 20th century period gave up after a few months and went back to their country of origin, often suffering from hunger and disease.
 1904 and 1914 - The "Second Aliyah" during which approximately 35,000 Jews immigrated, mostly from Russia and Poland.[514]
1904 and 1914 - The "Second Aliyah" during which approximately 35,000 Jews immigrated, mostly from Russia and Poland.[514]
Jewish history would not be complete without mentioning the Holocaust:
Approximately 9.5 million Jews lived in Europe in 1933, the year Hitler came to power.
In 1950, the Jewish population of Europe was about 3.5 million.
In 1933, 60 percent of all Jews lived in Europe. In 1950, most Jews (51 percent) lived in the Americas (North and South combined).
By 1945, most European Jews - two out of every three—had (6 million) been killed. 38% of the world's Jews died. Most of the surviving remnant of European Jewry decided to leave Europe. Hundreds of thousands established new lives in Israel, the United States, Canada, Australia, Great Britain, South America, and South Africa.
 2000 BC - The region that encompassed parts of modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and Jordan was home to various city-states, such as Jericho, Megiddo, and Hazor.
2000 BC - The region that encompassed parts of modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and Jordan was home to various city-states, such as Jericho, Megiddo, and Hazor.
Amorite Kingdoms: The Amorites were a Semitic people who established several kingdoms in Mesopotamia and the Levant.
1200 BC and 600 BC (Iron Age) -
Canaan, Judea, Israel, Syria, Samaria and Palestine are different names for overlapping territories.
Jews were the majority of the population of palestine fo the first 4 centuries of the Common Era (CE or AD)
Christians were a majority for the next few centuries.
Arabs dominated from the 13th century to the mid 20th century.
Jews became the majority in 1947 when the UN partitioned Palestine into Jewish and Palestinian-Arab areas.
See First century CE to 20th century in Jewish History above for information on
63 BCE - 636 CE - Roman rule/conflict,
132-135 2nd Jewish Revolt - Romans expel most Jews from Judea.
587 CE - Babylonian exile - Beginning of the Jewish diaspora (leaving Palestine),
By the 6th century Jews were a minority in Palestine
632-661, 1033, 1066 - Muslim Conflicts,
1096-1300 CE - Christian Conflicts (Crusades),
1453-1566 Ottoman Empire
1881 Zionism - Immigration (Aliyah) back to Palestine/Israel to start a Jewish homeland. ...
1917 Balfour Declarations stated that the government of Great Britain supported the establishment of a "Jewish national home" in Palestine.
1920 -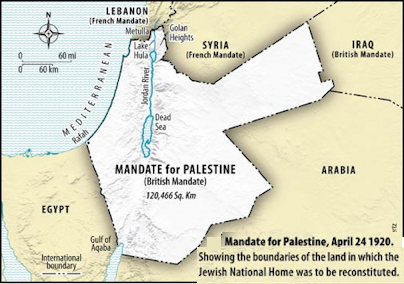 Creation of the British Mandate of Palestine
Creation of the British Mandate of Palestine
After World War One and the collapse of the Ottoman empire, territory known as Palestine - was marked out and assigned to Britain to administer by the victorious allied powers (soon after endorsed by the League of Nations).
This exacerbated tensions between the Arabs living in Mandate Palestine and the Jews who emigrated there during the Ottoman period.
1920 - The occupying European powers were realizing that they could no longer indefinitely occupy the middle east.
For the last two centuries, Jewish refugees from around the world were being forced out of the nations in which they were living. Jews from Russia and Ukraine, from Arab speaking nations of North Africa, and from other places in the middle east, were returning to their ancestral homeland.
1920 Map for the Palestine Mandate from the San Remo conference.
1922 - British Governance
Official end of the Ottoman Empire.
The League of Nations granted Britain the mandate to govern Palestine
1947 -  - the United Nations proposed a partition plan to create separate Jewish and Arab states in the territory. About 55% of the land, including most of Jerusalem, was given to the Jewish statem while the Palistian Arab state got 43%. the area around Jerusalem and Bethlehem, became the Jerusalem Internationalized territory under UN administration. It had a slight Arab majority.
The plan was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by Arab leaders, leading to the 1947–1949 Palestine War.
- the United Nations proposed a partition plan to create separate Jewish and Arab states in the territory. About 55% of the land, including most of Jerusalem, was given to the Jewish statem while the Palistian Arab state got 43%. the area around Jerusalem and Bethlehem, became the Jerusalem Internationalized territory under UN administration. It had a slight Arab majority.
The plan was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by Arab leaders, leading to the 1947–1949 Palestine War.
 1948 Arab-Israeli War (First Arab-Israeli War) -Israel's War of Independence (1947-1949)
1948 Arab-Israeli War (First Arab-Israeli War) -Israel's War of Independence (1947-1949)
The day after the 29 November 1947 adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine - which planned to divide the territory into an Arab state, a Jewish state, a civil war began. a civil war began.
6,373 Israelis were killed, 3,700-7,000 Arab fighters were killed and 3,000-13,000 Palestinian Arabs wer killed.
In 1949, with UN mediation, Israel concluded armistice agreements with Jordan, Egypt, Syria, and Lebanon, thus reaching an official cessation of hostilities of the first Arab-Israeli war that had started in May 1948.
On 15 May 1948, the civil war transformed into a conflict between Israel and the Arab states following the Israeli Declaration of Independence the previous day. Egypt, Transjordan, Syria, and expeditionary forces from Iraq entered Palestine. The invading forces took control of the Arab areas and immediately attacked Israeli forces and several Jewish settlements.
As a result of the war, the State of Israel controlled the area that the UN had proposed for the Jewish state, as well as almost 60% of the area proposed for the Arab state.
1967 - Six-Day War - Military hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours, who had been observing the 1949 Armistice Agreements signed at the end of the First Arab-Israeli War.
Israel capturing and occuping the Golan Heights from Syria, the West Bank (incl. East Jerusalem) from Jordan, and the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt.
It effectively doubled or tripled the size of territory under Israel's control.
776-983 Israelis were killed.
11,000 - 18,000 Egyptians, Syrians and Lebanese were killed
413,000 Palestinians were displaced
1978 - Camp David Accords - Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin meet in Camp David, Maryland, Agreements were signed by President Jimmy Carter, Egyptian President Anwar Sadat, and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin.
It results in a 1979 peace agreement between Egypt and Israel shifting the balance of power in the Middle East.
1982 - First Lebanon War. Israel Defense Forces (IDF) invaded southern Lebanon. The invasion followed a series of attacks and counter-attacks between the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) operating in southern Lebanon and Syrian leftists.
654 Israelis were killed, 1,000-2,400 PLO killed, 1,200 Syrians killed
1987-1993 First Intifada - Palestinian uprising against Israel. It resulted in the deaths of approximately 1.603 Palestinians and 359 Israelis.
1993 - Oslo Accords - Bill Clinton facilitated a meeting in 1993 between the Israeli prime minister, Yitzhak Rabin, and the Palestine Liberation Organisation leader, Yasser Arafat.
The Oslo II Accord divided the Israeli-occupied West Bank into three administrative divisions: the Palestinian enclaves as "Areas A and B" and the remainder, including Israeli settlements, as "Area C".

2000-2005 Second Intifada. the violence is estimated to have resulted in the deaths of approximately 3,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis.
2005 Israel pulls out of Gaza
2006 lebanon war (Israel-Hezbollah War or Second Lebanon War).
Hezbollah fighters fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence.
Israel attacked both Hezbollah military targets and Lebanese civilian infrastructure, including Beirut's Rafic Hariri International Airport.
Due to unprecedented Iranian military support to Hezbollah before and during the war,[41] some consider it the first round of the Iran-Israel proxy conflict, rather than a continuation of the Arab-Israeli conflict.
121 Israleis killed, Hezbollah ad Lebanese killed 290 (Hezbollah estimate), 600 (Israeli estimate)
2018 - President Trump moves the US Embasy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem.
Eugene Kontorovich claimed that the decision to shift the US embassy to this area is tantamount to the United States recognizing Israeli sovereignty over land that it captured in the Six-Day War in 1967. When the us announced the intention to move the embasy in 2017 the the UN General Assembly voted overwhelmingly during a rare emergency meeting today to ask nations not to establish diplomatic missions in the historic city of Jerusalem.
66-74 CE Roman Empire defeats Jews in 70 CE.
Jews killed or died from famine and disease
300,000-1 million
750-900 Civil wars drove Jewish emigration
Mass Islamization with Muslim majority
868-905 Mass Islamization of Samaritans
1096–1099 1st Crusade,
Crusaders massacre and enslave Jews and Muslims.
1187 Saladin defeats Crusaders;
spearheaded the Muslims against Crusaders
Figures in thousands.| Year | Jews | Christians | Muslims | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st c. | Majority | - | - | ~1,250 |
| 4th c. | Majority | Minority | - | >1,250 |
| 5th c. | Minority | Majority | - | |
| 12th - 14th c. - Crusades | ||||
| End 12th c. | Minority | Minority | Majority | >225 |
| 14th c. | Minority | Minority | Majority | 150 |
| 1533-1539 | 5 | 6 | 145 | 156 |
| 1553-1554 | 7 | 9 | 188 | 205 |
| 1690-1691 | 2 | 11 | 219 | 232 |
| 1800 | 7 | 22 | 246 | 275 |
| 1890 | 43 | 57 | 432 | 532 |
| 1914 | 94 | 70 | 525 | 689 |
| 1922 | 84 | 71 | 589 | 752 |
| 1931 | 175 | 89 | 760 | 1,033 |
| 1947 | 630 | 143 | 1,181 | 1,970 |
See slso Jewish Virtual Library | jewishwikipedia.info
Source: Jewish & Non-Jewish Population of Israel/Palestine | JewishVirtualLibrary
The accuracy of the Jewish Virtual Library (JVL) is debated; while it presents itself as a factual resource with numerous articles and primary documents, critics point to a significant pro-Israel bias and a lack of objectivity, leading the Wikipedia community to prohibit its use as a source for most situations. While some sources and reviewers have praised the JVL for its comprehensive nature, others argue its content omits key facts and perspectives, particularly in sections like "Myths & Facts"
Table needs to be update with Muslims from above
| Year | Jews (core population) | Non-Jews | Total Population | % Jewish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | 543,000 | 1,267,037 | 1,810,037 | 30.0% |
| 1947 | 630,000 | 1,324,000 | 1,970,000 | 32.0% |
| 1948 | 716,700 | 156,000 | 872,700 | 82.1% |
| 1950 | 1,203,000 | 167,100 | 1,370,100 | 87.8% |
| 1955 | 1,590,500 | 198,600 | 1,789,100 | 88.9% |
| 1960 | 1,911,300 | 239,100 | 2,150,400 | 88.9% |
| 1965 | 2,299,100 | 299,300 | 2,598,400 | 88.5% |
| 1970 | 2,582,000 | 440,100 | 3,022,100 | 85.5% |
| 1975 | 2,959,400 | 533,800 | 3,493,200 | 84.7% |
| 1980 | 3,282,700 | 639,000 | 3,921,700 | 83.7% |
| 1985 | 3,517,200 | 749,000 | 4,266,200 | 82.5% |
| 1990 | 3,946,700 | 875,000 | 4,821,700 | 81.9% |
| 1995 | 4,522,300 | 1,090,000 | 5,612,300 | 80.6% |
| 2000 | 4,955,400 | 1,413,900 | 6,369,300 | 77.8% |
| 2005 | 5,313,800 | 1,676,900 | 6,990,700 | 76.0% |
| 2010 | 5,802,900 | 1,892,200 | 7,695,100 | 75.4% |
| 2015 | 6,217,400 | 2,078,000 | 8,295,400 | 75% |
| 2020 | 6,870,000 | 2,421,000 | 9,291,000 | 73.9% |
| 2021 | 6,998,000 | 2,452,000 | 9,450,000 | 74.1% |
| 2022 | 7,101,400 | 2,560,000 | 9,662,000 | 73.5% |
| 2023* | 7,181,000 | 2,614,000 | 9,795,000 | 73.3% |
Population:
The latest Israeli census was conducted by Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2019. Israeli census excludes the Gaza Strip. It also excludes all West Bank Palestinian localities.
Israeli areas are 79% Jews and others and 21% Arabs.
The U.S. government estimates that 3 million Palestinians live in the West Bank and 2 million in the Gaza Strip.
In 2021 over 705,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank (20% of the population), of which approximately 238,000 live in East Jerusalem.
Who lives where:

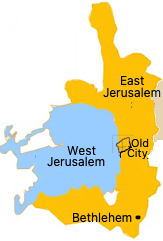
See Jerusalem
The Jewish Quarter is one of the four traditional quarters of the Old City of Jerusalem. The area lies in the southwestern sector of the walled city wesst of the Tempel Mount.
Israel captured East Jerusalem during the 1967 Six-Day War.
It is home to numerous yeshivas and synagogues, and the site of two historical mosques.
c. 2021 Population:
Millions
| Arabs | Jews | other | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Israel | 2.1 (27%) | 6.7 (88.2%) | 0.5 (5.4%) | 9.3 |
| Palestine | Jewish settlers | |||
| West Bank | 3.2 (41% *) | 0.7 (18% †) | (2%) | |
| East jerusalem | 0.4 (5% *) | 0.2 (33% †) | ||
| Gaza | 2.2 (28%) | 0 | (< 1%) | |
| Total Palestine | 5.8 (73%) | 0.9 (15%) | 6.7 | |
| Total Both | 7.9 (49%) | 7.6 (48%) | 0.5 (3%) | 16 |
The terrorist organizations in Gaza, Hamas, ISIS and Islamic Jihad are Sunni who were trained armed and funded by the Republic of Iran which is 61-64% Sunni.
85% of the worlds Muslims are Suni
See Islam
Israel has a population of just over 9 million, including around 7 million Jewish citizens and 2 million Israeli Arabs.
Israel-Palestine has a population of over 14 million, about half of whom are Jews and half Muslims (as well as a small minority of Christians: around 200,000).
Source: Le Modnde Oct, 2023
The World Fact Book | CIA: Israel. West Bamk, Gaza Strip
Where are the Jews in 2023
Israel 6.7 M 45.4% US 5.7 M 38.7% France 450,000 3.1% Canada 392,000 2.7% Other 1.5 M 10.2% Total 14.7 M
Jewish Virtual Library in 2023 The Jewish population is 7,181,000 (73.3%), and 2,065,000 (21.1%) are Arabs. Those identified as "others" make up 5.6% of the population (549,000 people).
the figures only include citizens of Israel and not Palestinians living in the disputed territories.
Terminology:
According to Palestinian citizens of Israel | wikipedia
How to refer to the Arab citizenry of Israel is a highly politicized issue, and there are a number of self-identification labels used by members of this community.[13][14] Generally speaking, supporters of Israel tend to use Israeli Arab or Arab Israeli to refer to this population without mentioning Palestine, while critics of Israel (or supporters of Palestinians) tend to use Palestinian or Palestinian Arab without referencing Israel.
According to The New York Times, most preferred to identify themselves as Palestinian citizens of Israel rather than as Israeli Arabs, as of 2012.
Administration:
Palestinian Authority currently administers some 39% of the West Bank. 61% of the West Bank remains under direct Israeli military and civilian control. East Jerusalem was unilaterally annexed by Israel in 1980, prior to the formation of the PA. Since 2007 Gaza has been governed by the Hamas Government in Gaza.
Israeli Settlement:
Following the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel occupied a number of territories. It took over the remainder of the Palestinian Mandate territories of the West Bank including East Jerusalem, from Jordan which had controlled the territories since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, and the Gaza Strip from Egypt, which had held Gaza under occupation since 1949. From Egypt, it also captured the Sinai Peninsula and from Syria it captured most of the Golan Heights,
Over 670,000 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank, of which approximately 220,000 live in East Jerusalem.
As of January 2023, there are 144 Israeli settlements in the West Bank, including 12 in East Jerusalem.
See Israeli settlement | wikipedia
Although PA laws theoretically apply in the Gaza Strip, the PA does not exercise authority there, and Hamas continues to exercise de facto control over security and other matters.
Israel evacuated and dismantled the 18 Sinai settlements following the 1979 Egypt-Israel peace agreement and all of the 21 settlements in the Gaza Strip, along with four in the West Bank, in 2005 as part of its unilateral disengagement from Gaza.
East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights have been effectively annexed by Israel, though the international community has rejected any change of status and considers each occupied territory.
Since June 2007, there have been two separate administrations in Palestine, one in the West Bank and the other in the Gaza Strip. The government on the West Bank was generally recognised as the Palestinian Authority Government. On the other hand, the government in the Gaza Strip claimed to be the legitimate government of the Palestinian Authority.
Legislative elections were held in the Palestinian territories in 2006 in order to elect the second Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC), the legislature of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA).
Hamas got 44% of the vote. Fatah got 41%.
The United States, Canada, the European Union, Japan and Israel classify Hamas as a terrorist organization and do not recognize the government. Hamas government is not recognized by the Ramallah administration of the State of Palestine.
I couldn't find any simple explanation of this.
See Politics of Palestine | Wikipedia
Hamas support:
The Dec. 2023 issue of Stanford Report says,
"A report in Arab Barometer's Survey of Palestinians found that About 23% of respondents said they have a great deal or quite a lot of trust in Hamas; 52% had no trust at all in Hamas."
Other reports showed more support for Hamas in the West Bank and Gaza.
In 2012, the U.N. General Assembly overwhelmingly approved the de facto recognition of the sovereign state of Palestine when it upgraded the Palestinian Authority's U.N. observer status to non-member state.
The 193-member U.N. General Assembly on Tuesday allowed the Palestinians to act more like a full U.N. member state during meetings in 2019.
See UN Allows Palestinians to Act More Like Full Member in 2019 | Voice of America (VOA)
Hamas, an acronym for the Islamic Resistance Movement, was founded as an offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood in 1987 on three pillars: religion, charity and the fight against Israel - although arguably its earliest enemy was Fatah, Yasser Arafat's rival Palestinian faction.
It is headquartered in Gaza.
After the 2006 Palestinian elections in which Hamas-backed candidates won the largest share of the vote, it seized power.
The United States and European Union have designated Hamas a terrorist organization because of its armed resistance against Israel, which has included suicide bombings and rocket attacks.
See "What is Hamas, the militant group that rules Gaza?" | The Guardian
The border around the Gaza Strip has grown into a semi-permanent structure with security fences and concrete walls set deep into the ground to prevent tunnelling - after Hamas militants launched a series of raids from tunnels into Israel in 2014. However, Hamas militants again breached the security barriers above ground in the biggest attack of its kind on 7 October, 2023.
On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel, using rockets, paragliders, motorboats, and ground infiltrators to target civilian and military sites across the country.
The massacre of more than 1,200 Israeli citizens the vast majority of them civilians. They also took hostiges.
It was the largest and most deadly attack by Hamas, a Palestian terrorist group, in it's history.
Israel formally declared war against Hamas as it battles to push militants off its soil.
They imposed a "complete siege" on the Gaza Strip, cutting off the water supply, food and electricity
The attack also sparked fears of a wider regional war, as Iran and Hezbollah, a Shiite Muslim political party and militant group based in Lebanon, expressed their support for Hamas and threatened to join the fight if Israel expanded its attacks to Lebanon or Syria
There are a dozen web pages with Israel-Palestine Maps covering the last 3,000 years.
Here is a recent one.
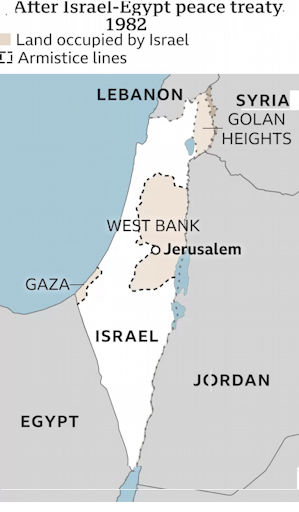
Source: Israel's borders explained in maps | BBC
Palestine's status in the UN (2023) is a "non-member state". not a Nation.
Palestine is not a country and does not appear as such on most maps.
Palestinians current (2023) status in the UN is a "non-member state".
About 250,000 Palestinians live in Israel proper.
The map below
from Alison Weir's book A Synopsis of the Israel/Palestine Conflict - IfAmericansKnew.org, which is popular on the internet shows the decline of areas ruled by Arabs.
See The origin of the State of Israel in maps, Merrimack Valley Havurah
Brief History after WW I
The 1930s - saw an escalation in Arab-Jewish violence in Palestine.
Britain handed the problem to the United Nations, which in 1947 proposed partitioning Palestine into two states - one Jewish, one Arab - with the Jerusalem-Bethlehem area to become an international city. The plan was accepted by Palestine's Jewish leadership but rejected by Arab leaders.
1947
in May 1948
Israel declared independence. Five Arab armies attacked believing they could destroy the
State. The UN had no troops and no plan to enforce its partition proposals. Israel fought
back and survived a year of fighting with a larger area. Armistice lines were drawn up in
1949 on the assumption they would be temporary, leaving the West Bank under Jordanian
occupation and Gaza occupied by Egypt.
The Jewish leadership in Palestine declared the establishment of the State of Israel on 14 May 1948, the moment the British mandate terminated, though without announcing its borders.
Links:
The question of Palestine | UN
The Merrimack Valley Havurah. (see below) says it is not accurate because "There was no Arab nation of Palestine ". This is true, Palestine's status in the UN (2023) is a "non-member state". not a Nation.
It has some good information but is biased in favor of the Palestinians and critical of US's involvement in creating the state of Israel.
The last map shows Israeli occupied areas in the West Bank as part of Israel, which is not technically true.
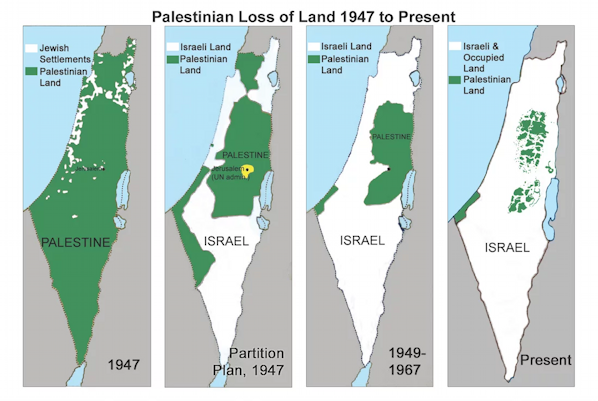
The Merrimack Valley Havurah is a Jewish community or group based in the Merrimack Valley region of Massachusetts who meet over coffee and tea to discuss Torah, or ethical/social issues, through the lens of Judaism's classic texts.
They include this map:

The terms of the mandate entrusted Britain with establishing in Palestine "a national home for the Jewish people", so long as doing so did not prejudice the civil and religious rights of non-Jewish communities there.
The following day Israel was invaded by five Arab armies, marking the start of Israel's War of Independence. The fighting ended in 1949 with a series of ceasefires, producing armistice lines along Israel's frontiers with neighbouring states, and creating the boundaries of what became known as the Gaza Strip (occupied by Egypt) and East Jerusalem and the West Bank (occupied by Jordan).
Glossary:
See "How Judaism Became a Religion," by Leora Batnitzsky.
It initially sought to establish an Arab state over the entire territory of Palestine.
However, in 1993, the PLO recognized Israeli sovereignty with the Oslo I Accord, and now only seeks Arab statehood in the Palestinian territories (the West Bank and the Gaza Strip.
US Israel SupportYour Guide to Understanding the Roots of the Israel-Hamas War | Bloomberg
Israeli-Palestinian peace process
What are the roots of the Israel-Palestine conflict? | The Guardian
Israel's borders explained in maps | BBC, October 2023
What is Hamas, the militant group that rules Gaza? | The Guardian
The Middle East after World War I
Remapping Europe and the Middle East after World War I
Israel-Palestine conflict: A brief history in maps and charts | Al Jazeera
What's the Israel-Palestine conflict about? A simple guide | Aljazeera
Arab Israeli Wars
Land of Israel | Wikipedia
Jewish Success
Two Palestinian American writers talk about what it's like to be Palestinian American in the U.S | NPR Code Switch nov 15, 2023
Jewish Diaspora and Occupation of the Holy Land
Judaism, Jewish history, and anti-Jewish prejudice: An overview| Strom Center for Jewish Studies, U. Washington
World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples - Egypt : Jews of Egypt
Anti-Semitism