This is a new topic where I am just throwing things that have to do with a person's relationships and mental health.
Contents:
Activities for Improving Mental Health
Ailments - Classification:
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
American Psychiatric Association
Depression
Psychotherapy
People (Freud, Jung, Piaget, Maslow, ...
Personality - Consciousness -Emotional Intelligence
See other links below.
Feel Good Brain Chemicals And Activities To Produce Them
Meditation
Mindfulness
Feel Good Brain Chemicals And Activities To Produce Them
Mental Illness can be classified as:
neurosis, a mild disorder that causes distress but does not interfere greatly with a person's everyday activities (e.g. anxiety and personality disorders) and
psychosis, a severe mental disorder that prevents the individual form functioning in a normal manner (e.g. Schizophrenia and manic-depressive disorder).
In any year, 10 percent of Americans--some 17 million people--suffer episodes of major depression.
American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic Classification - Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM)- Fourth Revision
- Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, or Adolescence: (Retardation, Learning, Communication, ...)
- Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic and Other Cognitive Disorders:
- Mental Disorders Due to a General Medical Condition:
- Substance-Related Disorders: (Alcohol, Amphetamine, Caffeine, Cannabis, Cocaine, Hallucinogen, Inhalant, Nicotine, Opioid, Phencyclidine, Sedative, Hypnotic, or Anxiolytic
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: (Delusional Disorder, )
- Mood Disorders: (Depression, ...)
- Anxiety Disorders: (Acute Stress, Agoraphobia, Phobias [claustrophobia, acrophobia, arachnophobia, ...], ...)
- Somatoform Disorders: (Hypochondriasis)
- Factitious Disorders: (Intentionally feigning symptoms of another sick person)
- Dissociative Disorders: (Amnesia, )
- Sexual and Gender Identity Disorders: (Aversion, Hypoactive, Dysfunction, Exhibitionism, Fetishism, Pedophilia, Voyeurism, ...)
- Eating Disorders:
- Sleep Disorders:
- Impulse-Control Disorders Not Elsewhere Classified: (Intermittent Explosive Disorder, Kleptomania, Pathological Gambling, Pyromania)
- Adjustment Disorders: (Anxiety and Depression from significant life events)
- Personality Disorders: (Paranoid, Schizoid, Antisocial, Narcissistic, Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive-Compulsive, ...)
- Other: (Medication Induced Tremor or movement disorder, Relational problems, Child abuse, Bereavement, anti-social behavior)
- ESP - Extrasensory Perception
See: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) at PSYweb.com
See also Mental and behavioural disorders at the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
Other diseases/disorders related to the brain:
These are not categorized as mental illness, but are either caused by problems in the brain and nervous system or may have symptoms similar to other problems associated with mental illness.
Many are under Diseases of the nervous system (G00) in
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
- Strokes and Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA's) are ischemic - blockage of a blood vessel supplying the brain, and hemorrhagic - bleeding into or around the brain. Stroke patients may have difficulty controlling their emotions or may express inappropriate emotions. Depression is a common side effect which frequently goes untreated. Strokes can be caused by hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis (arterial sclerosis or hardening of the arteries) causing a clot (embolism) which travels from some other part of the body to the brain. Ischemic stroke can also occur when too much plaque (fatty deposits and cholesterol) clogs the brain's blood vessels.
- Parkinson's disease (PD) belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders, which are the result of the loss of dopamine-producing brain cells. The four primary symptoms of PD are tremor, or trembling in hands, arms, legs, jaw, and face; rigidity, or stiffness of the limbs and trunk; bradykinesia, or slowness of movement; and postural instability, or impaired balance and coordination. Approximately 20% of people with Parkinson's disease will develop dementia, usually after the age of 70.
- Lupus, an autoimmune disease causing inflammation of the connective tissues, can affect many parts of the body, including the joints, skin, kidneys, lungs, heart, nervous system, and blood vessels. It may have symptoms similar to some mental illnesses.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS), a disease of the central nervous system where communication between the brain and other parts of the body is disrupted. Many investigators believe MS to be an autoimmune disease. Most MS patients experience muscle weakness in their extremities and difficulty with coordination and balance. Approximately half of all people with MS experience cognitive impairments such as difficulties with concentration, attention, memory, and poor judgment.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease, attacks motor neurons located in the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord that serve as controlling units and vital communication links between the nervous system and the voluntary muscles of the body.
- Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain. There are many types of encephalitis, most of which are caused by infection with viruses. Mental symptoms include seizures, sudden severe dementia, memory loss, withdrawal from social interaction, and impaired judgement.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes (called meninges) that surround the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis may be caused by many different viruses and bacteria, or by diseases that can cause inflammation of tissues of the body without infection (such as lupus). Symptoms include changes in behavior such as confusion, sleepiness, and difficulty waking up.
- Lyme disease is caused by a bacterial organism that is transmitted to humans via the bite of an infected tick. Some problems which may not appear until weeks, months, or years after a tick bite, include decreased concentration, irritability, memory and sleep disorders, and nerve damage in the arms and legs.
- Hypoglycemia or an insulin reaction, is a problem with diabetics when blood glucose level drops below 60 to 70 mg/dl.
Mental symptoms can include; dizziness and confusion, irritability, personality change,
confusion or poor concentation.
- Huntington's disease (HD) results from genetically programmed degeneration of brain cells, called neurons, in certain areas of the brain. This degeneration causes uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual faculties, and emotional disturbance.
- Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella-like term used to describe a group of chronic disorders impairing control of movement that appear in the first few years of life and generally do not worsen over time.
- Cancer - Many cancers in other parts of the body will metastize and spread to the brain. About 50% of brain cancers are metastatic (secondary) as opposed to primary brain cancer which originates in the brain. Symptoms of brain cancer depend on the location in the brain; They can include: Behavioral and emotional changes, Impaired judgment, Memory loss, Reduced mental capacity (cognitive function), Drowsiness.
- Pituitary Tumors - (Tthe pituitary gland, a small organ--about the size of a dime and located in the center of the brain--which makes hormones that affect growth and the functions of other glands in the body.) Symptoms of pituitary tumors may include headaches, vision problems, nausea and vomiting.
- Hodgkin's disease is a type of lymphoma distinguished by the presence of a particular kind of cancer cell called a Reed-Sternberg cell; It can cause depression.
| Major Nervous System
Diseases
|
| Disease |
Number of Cases |
Cost per year |
| Chronic Pain |
97,000,000 |
$100 billion |
| Hearing Loss |
28,000,000 |
$56 billion |
| Depression Disorders |
20,500,000 |
$44 billion |
| Alzheimer's Disease |
4,500,000 |
$100 billion |
| Stroke |
4,700,000 |
$51 billion |
| Epilepsy |
2,500,000 |
$3.5 billion |
| Traumatic Head Injury |
5,000,000 |
$56.3 billion |
| Huntington's Disease |
30,000 |
$2 billion |
| Schizophrenia |
2,000,000 |
$32.5 billion |
| Parkinson's Disease |
1,000,000 to
2,000,000 |
$25 billion |
| Multiple Sclerosis |
2,500,000 |
$9.5 billion |
| Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury |
250,000 |
$10 billion |
| Reference: Brain Facts, Washington D.C.: Society
for
Neuroscience, 2005.
|
See: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) for others.
Books:
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), by the American Psychiatric Association
See:
National Alliance for Mental Illness (NAMI)
Mental illness at wikipedia.org
Information on Brain Disorders and Brain Diseases
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD)
at World Health Organization (WHO)
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) of the American Psychiatric Association.
Mental Illness at wikipedia.org
Famous Mental Health Consumers.
Psychotherapy is a treatment option for a number of mental disorders, including depression, dissociative identity disorder, eating disorders, generalized anxiety disorder, hypochondriasis, insomnia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and panic disorderwithout agoraphobia.
Treatments
Treatments include:
Psychotherapy
Psychodynamic psychotherapy:
The psychoanalytic method of Sigmund Freud (1856-1939), focuses on unconscious mental processes and their roots in the past.
See: Types of Psychological Treatment at GuideToPsychology.com
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) 1980
Since the 1980s, many therapists have begun to use cognitive-behavioral therapy to change clients' unhealthy behavior by replacing negative or self-defeating thought patterns with more positive ones.
They do not deny that problems may be rooted in the past but treat them differently.
Psychodynamic theories presume that the maladaptive cognitions arise from specific internal needs (such as the need for affection, acceptance, sexual gratification, etc.), or from unresolved developmental conflicts from childhood. The cognitive therapists presume that the maladaptive cognitions may arise from faulty social learning, or from a lack of experiences that would allow adaptive learning (such as the development of coping skills) to occur, or from dysfunctional family experiences, or from traumatic events, etc. In other words, psychologists using a cognitive therapy approach recognize that psychological problems such as depression can develop from a variety of life experiences, depending on the individual.
Cognitive therapy was developed by Aaron Beck developed cognitive therapy in the 1960s.
The treatment is based on the principle that maladaptive behavior (ineffective, self-defeating behavior) is triggered by inappropriate or irrational thinking patterns, called automatic thoughts. Instead of reacting to the reality of a situation, an individual automatically reacts to his or her own distorted view of the situation. Cognitive therapy strives to change these thought patterns (also known as cognitive distortions), by examining the rationality and validity of the assumptions behind them. This process is termed cognitive restructuring.
Behavior therapy focuses on observable behavior and its modification in the present, in contrast to
the Freudian Psychoanalytic method.
The therapy drew on a variety of theories and research, including the classical conditioning principles of the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), the work of American B. F. Skinner (1904-1990), and the work of psychiatrist Joesph Wolpe (1915-1997).
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) 1980
A psychological method developed by Marsha M. Linehan, a psychology researcher at the University of Washington, to treat persons with borderline personality disorder (BPD). DBT combines standard cognitive-behavioral techniques for emotion regulation and reality-testing with concepts of mindful awareness, distress tolerance, and acceptance largely derived from Buddhist meditative practice. DBT is the first therapy that has been experimentally demonstrated to be effective for treating BPD. Research indicates that DBT is also effective in treating patients who represent varied symptoms and behaviors associated with spectrum mood disorders.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) 2005
A unique intervention approach based on Relational Frame Theory (RFT) that
illuminates the ways that language entangles us into futile attempts to
wage war against our own inner lives.
Through metaphor, paradox, and experiential exercises clients learn how to
make healthy contact with thoughts, feelings, memories, and physical sensations
that have been feared and avoided. Clients gain the skills to recontextualize
and accept these private events, develop greater clarity about personal values,
and commit to needed behavior change.
See: ACT at ContextualPsychology.org
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT):
ECT has improved greatly over the years with medications given before the treatment that alleviates the effects of a severe seizure.
ECT is an effective form of treatment for people with depressions and other mood disorders. ECT may be used when a severely depressed patient has not responded to antidepressants, is unable to tolerate the side effects of antidepressants, or must improve rapidly.
The patient is given medications to induce sleep, relax the muscles. An electrical stimulus is administered through electrodes to the head. The electrical stimulus produces brain wave (EEG) changes that are characteristic of a grand mal seizure.
Other:
Psychosurgery
Paranormal
Aging and Happiness
Personality - Consciousness -Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence - Maturity - Well-being
Teen Stress
Cognitive Dissonance
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
Multitasking
Perfectionism
Brain Exercises
Intelligence and Age
Stress
Love
Marriage
Spirituality, Mindfulness, Personal Growth... references under Religion
Consciousness Models
We are Not Rational
Wilber's AQAL (all-quadrant, all-level) model in his "Theory of Everything".
Moral development and Conscience
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
Spiral Dynamics
Nature Nurture Issues - How much of abilities, behavior, ... is genetic vs environment.
See Personality - Success - Character on the society page
Personality
I am not a psychologist, but was always intrigued by the subject, trying to understand while some intelligent friends seemed to act or react in ways I found irrational.
Having been trained as a mathematician (I still remember how to prove that 1 + = 2) the fuzzy logic in these things are still perplexing to me.
Have all these theories helped us to get along better. I don't think so.
Greeks believed people fall into four temperamental categories - choleric, phlegmatic, sanguine and melancholic.
In the mid 20th century the British-born psychologist Raymond Cattell devised a personality test based on the idea that there are 16 personality factors including guilt-proneness and shrewdness.
Contemporary psychology has now settled on the idea there are in fact five main factors to personality, knows as the Five Factor Model (FFM) - extroversion, neuroticism (associated with anxiety and apprehension), conscientiousness, agreeableness, and openness (associated with creativity and insight). We all have a certain amount of each of these, more of some than others.
The NEO Personality Inventory-Revised | NEO PI-R questionnaire is an assessment of these.
See my Nature/Nurture - Genes vs Environment page for more on how these things get shaped in one's mind.
Psychometric Assessment:
Myers Briggs Personality Type Indicator
The personality type I was first exposed to was the Myers Briggs model, having been tested in corporate mamagement training sessions and a Church leadership seminar.
- Where you focus your attention - Extraversion (E) or Introversion (I)
- The way you take in information - Sensing (S) or INtuition (N)
- How you make decisions - Thinking (T) or Feeling (F)
- How you deal with the world - Judging (J) or Perceiving (P)
Isabel Briggs Myers' personality type theory is based on C. G. Jung's theory of psychological types.
Free Personality Test | 16Personalities
DISC (Dominance, Influence, Steadiness and Conscientiousness) is another personality type assessment similar to Myers Briggs which has become popular recently.
The Core Values Index (CVI) is another popular one.
The key to the CVI is its Repeat Score Reliability of 94.5%. This means if you took the CVI 5 year ago or 10 years from now, your CVI score will be virtually the same 95% of the time.
See:
Take CVI | Taylor Protocols
Core Values Index Assessment | MillennialCoaching.ca
Personality type A/B
Personality type is a modified version of the Jenkins Activity Survey originally designed to detect behaviors which lead to heart attacks.
- Type A personality generally refers to hard workers who are often preoccupied with schedules and the speed of their performance.
- Type B personalities may be more creative, imaginative, and philosophical.
Take a test at the Univ. of N. Carolina
See: Personaliy Theories by Dr. C. George Boeree, Psychology Department, Shippensburg University
Enneagram:
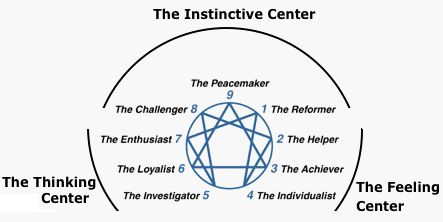
Enneagram - How the System Works -- The Enneagram Institute
Eclectic Energies Enneagram Tests
Wiltse and Palmer have suggested that similar ideas to the Enneagram of Personality are found in the work of Evagrius Ponticus, a Christian mystic who lived in 4th century Alexandria.
G. I. Gurdjieff is credited with making the enneagram figure commonly known.
Brain Exercises:
Recent studies have shown that you can improve your brain or forestal problems associated with aging by exercising your brain. Such techniques are called "brain fitness" or "cognitive training".
Some resources:
sharpbrains.com |
fitbrains.com |
lumosity.com |
cognifit.com
A gym in San Francisco (www.vibrantbrains.com), describes itself as a "health club for your brain" .
Psychology
- Freud, Sigmund (1856-1939)
-
"The Interpretation of Dreams"
Id - What we want to do
Superego - What we are told by society and parents that we should do
Ego - Resolve conflict between above
-
- Alfred Adler (1870-1937)
- The first well-known dissenter from Freud's school of thought. Adler became the father of what he called "individual psychology." He shifted the motivational emphasis from biological instincts to social relationships. (Adler is also considered a humanist.)
- Jung, Carl (1875-1961)
- He submitted that attention must be given to man's religious, aesthetic, and other such needs. (the seeds of modern day existentialism). He is also noted for his work with the concepts of introversion/extroversion and archetypes.
- Binet, Alfred (1857-1911)
-
He is most widely known for his contributions to intelligence.
- Horney, Karen (1885 - 1952)
-
- Goodenough, Florence (1886-1959)
- Draw-A-Man Man Test (1926).
A pioneer in psychology and the study of gifted children.
- Piaget, Jean (1896 - 1980)
- Genetic epistemology, meaning the study of the development of knowledge.
- Maslow, Abraham (1908-1970)
-
- Fromm, Erich (1900 - 1980)
-
- Erikson, Erik H. (1902-1994)
-
- Skinner, B. F. (1904 - 1990)
- Indiana U. and Harvard.
System is based on operant conditioning. A reinforcing stimulus following an action creates
tendency to repeat the behavior in the future.
Directories
Mental Health at: Google, Yahoo.
Relationships at: Google, Yahoo
See also: History of Neuroscience including Nobel Prize winners.
Other Links:
Philosophy - Intellect - The Mind and Ideas
Personal Characteristics
Nature/Nurture - Genes vs Environment
mental-health-matters
Meditation
Feel Good Brain Chemicals And Activities To Produce Them
Neuroscience
Metaphysics for Dummies
Religion and the human psyche or brain
Perceived Christian Hypocrisy
Nature-Deficit Disorder
Glossary by Thomas Hübl - Spiritual Teacher - Academy of Inner Science
Empty - Cluttered Desk
Procrastination
Architecture Mood Creativity
Ways Your Mate Can Affect Your Health
Depression and Anxiety Drugs
Return to Don's Home.
last updated 19 Mar 2006
 Mental Health- Relataionships - goals
Mental Health- Relataionships - goals
 Mental Health- Relataionships - goals
Mental Health- Relataionships - goals
