 Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Under Construction 
Health
 Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
|
|
| Heart Attack | Coronary Artery Disease | Cholesterol | Stents | Heart Bypass Surgery | Cardiac Rehab | Cardiovascular Disease | |
|
Under Construction | |
|
Background: A decade ago, the treatment of hypercholesterolemia (High cholesterol) and hypertension (High blood pressure) was expected to eliminate CAD by the end of the 20th century. Lately, however, that optimistic prediction has needed revision. Cardiovascular diseases are expected to be the main cause of death globally within the next 15 years owing to a rapidly increasing prevalence in developing countries and eastern Europe and the rising incidence of obesity and diabetes in the Western world. 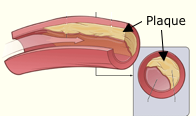 Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of major adverse cardiac events (MACE, generally defined as death, non-fatal acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting).
Cardiovascular diseases cause 38 percent of all deaths in North America and are the most common cause of death in European men under 65 years of age and the second most common cause in women.
Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of major adverse cardiac events (MACE, generally defined as death, non-fatal acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting).
Cardiovascular diseases cause 38 percent of all deaths in North America and are the most common cause of death in European men under 65 years of age and the second most common cause in women.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) also called Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is caused when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries (Atherosclerosis of heart arteries). The National Coronary Artery Disease Education Program's (NCEP) defines high-risk patients as those who have coronary heart disease or disease of the blood vessels to the brain or extremities, or diabetes, or multiple (2 or more) risk factors (e.g., smoking, hypertension) that give them a greater than 20 percent chance of having a heart attack within 10 years. Heart Attack (Myocardial infarction): Myocardial infarction occurs when the atheromatous process (accumulation of material in the inner layer of artery walls) prevents blood flow through the coronary artery. It was previously thought that progressive luminal (the inside space of a tubular structure) narrowing from continued growth of smooth-muscle cells in the plaque was the main cause of infarction.
There are two major causes of coronary thrombosis (blood clots): plaque rupture and endothelial (thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels) erosion. Plaque rupture, which is detectable in 60 to 70 percent of cases. Images from my cardiac catheterization showing 95% blockage of the Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery (the widow maker) before and after angioplasty and installation of a stent.
Terms: ACS - Acute Coronary Syndrome - An umbrella term for situations where the blood supplied to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked. e.g. heart attack, or unstable angina.
Angine pectoris - Chest pain. Stable angina refers to the more common understanding of angina related to myocardial ischemia. Angioplasty - A tube with a tiny balloon on the end is inserted thru the catheter. When the tube is in place, the doctor inflates the balloon to push the plaque outward against the wall of the artery, thus opening the artery for increased blood flow. Atheromatous process - Accumulation of material in the inner layer of artery walls. Atherosclerosis - A disease in which plaque (plak) builds up inside your arteries. Atherosclerosis can affect any artery in the body, including arteries in the heart, brain, arms, legs, pelvis, and kidneys. Catheter - CAD - Coronary Artery Disease - Atherosclerosis of the arteries supplying blood to your heart.. CHD - Coronary Heart Disease - Same as CAD LAD - Left Anterior Descending artery. Main heart artery on the left side. Lumen - The inside space of a tubular structure PCI - Percutaneous Coronary Intervention - Angioplasty
Stent - a small mesh tube that's inserted thru a catheter and expanded at the site of angioplasty. It forms a permanent scaffold to hold the coronary artery open . Links: Stents cholesterol What Is Atherosclerosis? - NHLBI, NIH Understanding coronary artery disease: tomographic imaging with intravascular ultrasound, Heart. 2002 Jul; Cardiac Rehab Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention-DHDSP|Home Page|CDC Return to Health |