Under Construction 
Contents: Most Spoken | Classification | Classical Written Languages | Printing/Writing
Ethnologue: Languages of the World from The Summer Institute of Linguistics (SIL) lists 7,200 primary language names and 39,491 alternate names and dialects.
Most Spoken
Ranking by number of native speakers at Ethnologue
Rank native/total
| Rank | Language Name | Speakers (M) | Official Language in
[1] |
| English | Native | Native | Total |
| 1/1 | Mandarin, ex. | 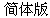 (simp) (simp) 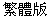 (trad) (trad)
| 885 | 1051 | PRC, ROC, [2] Singapore, |
| 2/5 | Spanish | Español ex. | 332 | 480 | Spain, Andorra, Central and South America (except Brazil), Cuba, Dominican Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Mexico, Puerto Rico |
| 3/2 | English | English | 322 | 980 | United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, United States, Canada, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Botswana, Brunei, Dominica, The Gambia, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Liberia, The Bahamas.
Non-exclusive: Cameroon, Canada, Hong Kong, India, Kenya, Kiribati, Kosovo, Lesotho, Malaysia, Malta, Pakistan, Philippines, Singapore, South Africa, Zimbabwe |
| 4/6 | Arabic |  ex. ex. | 206 | 323
[3] | Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Chad, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Western Sahara (SADR), Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen; |
| 5 | Bengali |  | 189 | | Bangladesh, India |
| 6/3 | Hindi | 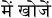 ex. ex. | 182 | 948 | India, Fiji |
| 7/8 | Portuguese | Português | 177 | 223 | Portugal, Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, East Timor, European Union, Guinea Bissau, Chinese S.A.R. of Macau, Mozambique, São Tomé and Príncipe |
| 8/7 | Russian
Cyrillic | 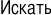 ex. ex. | 170 | 255 | Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Abkhazia, South Ossetia, Transnistria, and Gagauzia. |
| 9/10 | Japanese | 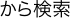 4ex. 4ex. | 125 | 130 | Japan, Angaur (Palau) |
| 10/11 | German | Deutsch ex. | 95 | 122 | Germany, Austria, European Union, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Switzerland, |
| 11 | Punjabi
or Panjabi | 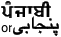 [5] [5] | 89 | | Western Panjabi - Punjab area of Pakistan 61M
Eastern Panjabi - Punjab (India), Haryana, Amritsar, Chandigarh and Delhi - 28 M |
| 12 | Wu | 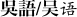 | 77 | | vernacular language of Shanghai is a dialect of Wu |
| 13/4 | French | Français Ex. | 77 | 500 | France, Switzerland, parts of Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco, Canada (Quebec), French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Barthelemy, St. Martin, Saint-Pierre, Hati, NW Africa (Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Djibouti, Guinea, Madagascar, Mali, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, ...), Laos, Lebanon, Vanuatu, French Polynesia |
| 14 | Javanese | | 70 | | Java (Indonesia) |
| 15 | Korean | 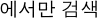 | 70 | | N. & S. Korea |
| 16 | Vietnamese | 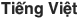 | 67 | 86 | Vietnam |
| 17 | Telugu | | 66 | 86 | India |
| 18/12 | Cantonese | 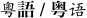 | 66 | 100 | Hong Kong SAR and Macau |
| 19 | Marathi | | 64 | 71 | Maharashtra & Goa State, India |
| 20 | Tamil | | 63 | 72 | India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Singapore |
| 21 | Italian | Italiano Ex. | 61 | | Italy, Switzerland, European Union, San Marino, Slovenia, Somalia |
| 22 | Min | 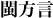 | 59 | | Fujian province in China and migrants in Guangdong, Hainan, Taiwan and other areas. |
| 23 | Turkish | Türkçe | 59 | 75 | Turkey, Cyprus, Kosovo, Republic of Macedonia |
| 24/11 | Urdu | 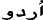 | 58 | 104 | Pakistan; India (Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttar Pradesh) |
| 25 | Persian: (Farsi, Dari, ...) | 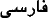 ex. ex. | 49 | | Iran, Tajikistan, Afghanistan |
| 26 | Polish | 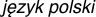 | 44 | | Poland, European Union |
| 27 | Gujarati | | 44 | | India |
| 28 | Ukrainian | | 41 | | Ukraine |
| 29 | Nepali | | 40 | | Nepal, Sikkim (India) |
| 35 | Thai | 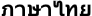 | 20 | | Thailand |
| 37 | Pashto | | 27 | | Afghanistan |
| /9 | Indonesian | | 17 | 200 | Indonesia |
| 52 | Greek | 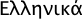 | 12 | | Greece, Cyprus |
| | Swedish ex. | 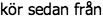 | | 10 | Sweden |
| 80 | Tibetan | 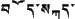 | 6 | | Tibet (China) |
| 81 | Hebrew | 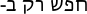 alphabet wikipedia alphabet wikipedia | 5 | | Israel |
| 87 | Armenian | 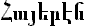 | 5 | | Armenia |
Source: List of languages at wikipedia
1. Many countries have several official languages. e.g. Canada (English, French); Switzerland (German, Italian, French); India (Hindi, English and 21 others).
2. PRC - Peoples Republic of China (Mainland) - Simplified characters
ROC - Taiwan - Traditional characters
3. 323 million people in Arab countries
4. combination of three different types of scripts: Chinese characters, kanji, and two syllabic scripts, hiragana and katakana.
5. Panjabi has two writing systems Gurmukhi and Shahmukhi.
See also: Alphabets at omniglot.com
and Languages supported by google
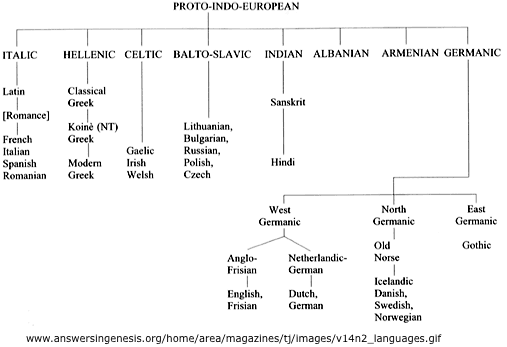
* Indo-European
Indo_Iranian
Hindi 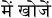 , Urdu (Pakistan, India, Afghanistan) , Urdu (Pakistan, India, Afghanistan) 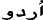 , Farsi (Iran) , Farsi (Iran) 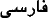 ,
Kurdish, Bengali (Bangladesh, India), Punjabi , Pashto (Afghanistan), Marathi, ...
Hellenic
Greek ,
Kurdish, Bengali (Bangladesh, India), Punjabi , Pashto (Afghanistan), Marathi, ...
Hellenic
Greek 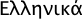 Germanic
Deutsch (German), English, Afrikaans (South Africa and Namibia)
Romance
Español (Spanish), Français (French), Italiano (Italian), Português (Portuguese)
Northern Germanic - Scandinavian Causasian
Svenska (Swedish), Danish, Norwegian, ...
Norse - Old Norse
Caucasian
(classified into several language families,
with little or no discernible affinity to each other.)
Georgian, Chechen, ...
Slavic and Balto-Slavic
Russian
Germanic
Deutsch (German), English, Afrikaans (South Africa and Namibia)
Romance
Español (Spanish), Français (French), Italiano (Italian), Português (Portuguese)
Northern Germanic - Scandinavian Causasian
Svenska (Swedish), Danish, Norwegian, ...
Norse - Old Norse
Caucasian
(classified into several language families,
with little or no discernible affinity to each other.)
Georgian, Chechen, ...
Slavic and Balto-Slavic
Russian  (Cyrillic),
Polska, Czech, Slovak, Croatian, Ukrainian...
* Uralic
Finnish, Estonian, Hungarian
* Afro-Asiatic
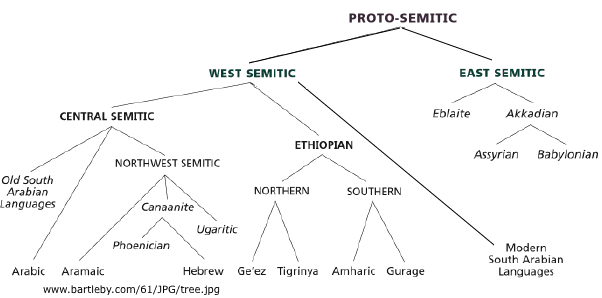
Semitic
Arabic (Iraq) (Cyrillic),
Polska, Czech, Slovak, Croatian, Ukrainian...
* Uralic
Finnish, Estonian, Hungarian
* Afro-Asiatic
Semitic
Arabic (Iraq)  , Hebrew , Hebrew 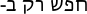 , Amharic (Ethopia),
Aramaic, Coptic
Chadic
Hausa (Niger)
Cushitic
Oromo (Ethopia),
Ancient Egyptian (The language of modern day Egypt is Egyptian Arabic)
* Niger-Congo-Kordofanian and Nilo-Saharan
Yoruba (Nigeria), Swahili, Chichewa (south-central Africa), Somali, ...
* Dravidian (Southern Asia)
Tamil, Telugu (India), Malayalam,
* Altaic languages
Türkçe (Turkic, Turkish), Mongolic, sometimes includes Japonic
* Japonic
Japanese , Amharic (Ethopia),
Aramaic, Coptic
Chadic
Hausa (Niger)
Cushitic
Oromo (Ethopia),
Ancient Egyptian (The language of modern day Egypt is Egyptian Arabic)
* Niger-Congo-Kordofanian and Nilo-Saharan
Yoruba (Nigeria), Swahili, Chichewa (south-central Africa), Somali, ...
* Dravidian (Southern Asia)
Tamil, Telugu (India), Malayalam,
* Altaic languages
Türkçe (Turkic, Turkish), Mongolic, sometimes includes Japonic
* Japonic
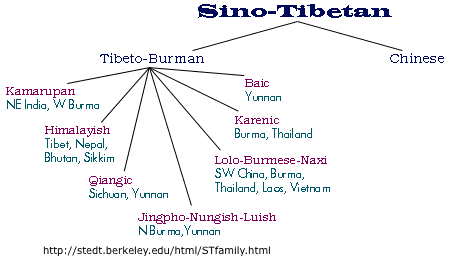
Japanese 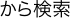 * Sino-Tibetan
Chinese: Mandarin, Cantonese, Wu (Shanghai), Hakka, Xiang, Gan
Min (A group of dialects of the Chinese language spoken in the southeastern
Chinese province of Fujian as well as by migrants from this area)
Taiwanese (dialect of Min Nan)
Written: Chinese Traditional
* Sino-Tibetan
Chinese: Mandarin, Cantonese, Wu (Shanghai), Hakka, Xiang, Gan
Min (A group of dialects of the Chinese language spoken in the southeastern
Chinese province of Fujian as well as by migrants from this area)
Taiwanese (dialect of Min Nan)
Written: Chinese Traditional  , Chinese Simplified , Chinese Simplified 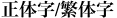 Tibetan
Tibetan 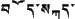 *Sino-Xenic
Sometimes Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese are listed in this category
* Tai-Kadai
Thai
*Sino-Xenic
Sometimes Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese are listed in this category
* Tai-Kadai
Thai  * Austronesian
Indonesian, Filipino (based on Tagalog), Malay
* Austronesian
Indonesian, Filipino (based on Tagalog), Malay  , Javanese,
* Isolates (Cannot be classified)
Asia
Korean , Javanese,
* Isolates (Cannot be classified)
Asia
Korean  (Sino-Xenic)
Europe
Euskara - Basque - unknown origin.
it shows no ressemblance to languages in neighbouring countries.
Many think it is a very old language because there are words,
such as that for axe ("aizkora" or "haizkora") for example,
that have the same root as the word rock. (Sino-Xenic)
Europe
Euskara - Basque - unknown origin.
it shows no ressemblance to languages in neighbouring countries.
Many think it is a very old language because there are words,
such as that for axe ("aizkora" or "haizkora") for example,
that have the same root as the word rock.
Language Trees:
Cuneiform -
3,500 BCE 1,000 glyphs
Earliest known form of written expressiion. Created by the Sumerians and continued through the end of the Babylonian and Assyrian empires.
300–600 cuneiform symbols.
In 1933 25,000 clay tablets in Akkadian language written in cuneiform were discovered in Syria. They were dated to the last 50 years of Mari's independence (ca. 1800-1750 BC). Mari (modern Tell Hariri, Syria) was an ancient Sumerian and Amorite city, located on the Euphrates river near the Iraqi border.
Cuneiform script underwent considerable changes over a period spanning three millennia. In the course of the 3rd millennium BC the script became successively more cursive, and the pictographs developed into conventionalized linear drawings, the number of characters in use also refined from around 1,000 unique characters in the 3,000 BCI to around 400 characters in 1,000 BCE (Hittite cuneiform). See Cuneiform at wikipedia. |
 |
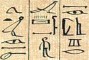
Egyptian Hieroglyphics -
3,200 BCE - 400 CE 700 glyphs.
Replaced by coptic.
See: Ancient Egyptian scripts at omniglot
|
 |
Writing instruments -
2,000 BCE
Writing was originally done by chiseling pictures into stone or wedging pictographs into wet clay.
2,000 BCE - Egyptian "Prisse Papyrus" oldest parchment / pypyrus
1200 BCE - Chinese invented and perfected 'Indian Ink'; Originally designed for blacking the surfaces of raised stone-carved hieroglyphics.
Dead Sea Scrolls 150 BCE - 68 CE
See more writing/printing/word processing below.
|
Akkadian - 2,500 BCE - 100 CE.
Spoken in ancient Mesopotamia, particularly by the Assyrians and Babylonians.
|
Sanskrit -
1,700 BCE-Present
A classical language of India, a liturgical language of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, and one of the 23 official languages of India.
| 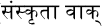
|
|
Alphabets replaced pictographs 1700 = 1500 BCE |
Old Chinese -
1,500 BCE
See: Chinese at omniglot
|
 |
| Greek - 1,400 BCE | Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ω
α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ω
| Hebrew -
900 BCE -
The first written evidence of distinctive Hebrew, the Gezer calendar, dates back to the 10th century BCE. One of the Semitic languages.
It is the main language of the "Old Testiment" or Hebrew Bible. The Dead Sea Scrolls were written mainly in Hebrew, but some are in Aramaic.
See: Hebrew alphabet at omniglot
|
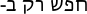 |
Aramaic -
900 BCE -
The Early Aramaic or Proto-Hebrew alphabet was developed sometime during the late 10th or early 9th century BC and replaced Assyrian cuneiform as the main writing system of the Assyrian empire. One of the Semitic languages.
This language appears in the Old Testament of the Bible in five places: Ezra 4:8-6:18, Ezra 7:12-26, Daniel 2:4-7:28, Jer. 10:11 and Gen. 31:47, and is the main language of the Talmud (Record of Jewish law, ethics, ...). Aramaic was the native language of Jesus.
See: Aramaic alphabet at omniglot.
|
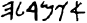 |
Celtic - 1,000 BCE - During the 1st millennium BC, variations were spoken across Europe; Today, Celtic languages are limited to a few areas in the British Isles, eastern Canada and Patagonia.
Divided into sub-families: Gaulish, Celtiberian, Goidelic and Brythonic (Welsh, Breton, Cornish, possibly Pictish and others.
| Goidelic (Gaelic) - A type of Celtic language
100 BCE - 1,800 CE
Goidelic-speaking Milesians invaded Ireland in the 1st or 2nd century BC.
Goidelic is generally divided into: Irish (Gaeilge), Scottish Gaelic (Gàidhlig), and Manx (Gaelg), in the Isle of Man.
Classical Gaelic, was used as a literary language in Ireland until the 17th century and in Scotland until the 18th century.
In Scottish English, Gaelic is pronounced [ˈgaːlɪk]; outside Scotland, it is usually pronounced /ˈgeɪlɪk/.
See:
Gaelic at WorldLanguage.com
Written text in old and current font.
|
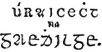 |
Latin - 800 BCE
The formal language of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire.
See: Latin alphabet at omniglot
|
 |
Coptic - 600 BC - 1,600 CE
Replacement for ancient Egyptian around 600 BC until it gave way to Arabic in the 17th century. The Coptic alphabet is a slightly modified form of the Greek alphabet used in Egypt.
See: Coptic at omniglot
| Etruscan - 600 BCE
A Western variety of the Greek alphabet brought to Italy by Euboean Greeks, who lived in Etruria (current area around Tuscany).
| Ethiopic (Ge'ez alphabet) - 500 BCE - present.
The classical language of Ethiopia which is still used as a liturgical language by Ethiopian christians and the Beta Israel Jewish community of Ethiopia.
See: Ethiopic alphabet at omniglot
| Mayan
300 BCE - 1,500 CE
See: Mayan Script at omniglot
|
 |
BCE - Before Common Era (same as BC)
See:
Classical Languages at Excite UK,
The Early History of Indo-European Languages
Ancient and Extinct languages in the ISO 639-3 Standard at linguistlist.org
Writing - Printing - Word processing
3,500 BCE - Sumerian Cuneiform glyphs on clay tablets
3,200 BCE = Egyptian Hieroglyphics glyphs on clay tablets
2,000 BCE - Egyptian "Prisse Papyrus" oldest parchment / pypyrus
1200 BCE - Chinese invented and perfected 'Indian Ink'; Originally designed for blacking the surfaces of raised stone-carved hieroglyphics.
105 A.D. Wood-fiber paper was invented by Tsai, Lun in China.
1040 - printing with wooden and ceramic movable type - China.
late 14th century - Paper mills in Europe increase use of paper.
1436 Gutenberg develops the printing press.
1714 The first patent for a 'writing machine' was given to Henry Mill of England
1868 Christopher Sholes, Carlos Glidden and Samuel Soule patent a type writing machine.
1872 Thomas Alva Edison builds first electric typewriter.
1873 Christopher Latham Sholes builds typewriter that Remington & Son puts into production.
1886 - Linotype typesetting machine. Uses a process known as "hot metal" typesetting.
1964 IBM brought out the MT/ST (Magnetic Tape/Selectric Typewriter)
1964 RUNOFF markup language for computer typesetting developed for MIT's CTSS OS
1970's - Phototypsetting "cold type" replaces "hot metal". It uses photographic paper.
1972 Lexitron and Linolex develop a word processing system, with video display screens
1974 WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) word processing program Bravo developed at Xerox PARC.
1979 - Rob Barnaby wrote WordStar for CP/M to run on personal computers.
1983 - Microsoft word for DOS. Showed bold and italics, but not multiple typefaces.
1984 - MacWrite WYSIWYG word processor released with the first Macintosh.
1993 - First popular HTML (Hypertext markup language) web browser, NCSA Mosaic, developed by Marc Andreessen at UIUC.
More Examples:
Examples from Google:
List of languages in 2009:
Deutsch, Español, Français, Italiano,
Chinese Traditional  , Chinese Simplified , Chinese Simplified 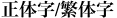 ,
Japanese ,
Japanese  ,
Korean ,
Korean  ,
Hindi ,
Hindi  ,
Arabic ,
Arabic  ,
Hebrew ,
Hebrew 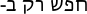 ,
Russian ,
Russian 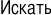 ,
Nederlands, Polska, Svenska, ... ,
Nederlands, Polska, Svenska, ...
Languages and regions - support.google.com/News Help 2014
We have more than 70 regional editions of Google News in many different languages. To change editions when you're on the Google News homepage, simply select your preferred edition from the drop down menu at the top of the page.
|

