Under Construction 
Contents: Water on the knee | Ligament Injuries
Water on the knee:
Knee effusion causes swelling, pain and stiffness.
The knee joint normally contains less than one ounce of lubricating fluid. Injury or inflammation of the knee joint causes extra fluid to collect there.
Causes:
Injuries:
Damage to any part of your knee can cause the painful buildup of excess joint fluid. Examples of traumatic injuries that cause fluid buildup in and around the knee joint are:
- Broken bones
- Meniscus cartilage tear
- Ligament tear
- Overuse injuries
Diseases and conditions:
Underlying diseases and conditions that may produce fluid buildup in and around the knee joint include:
See others at Water on the knee: Causes - MayoClinic.com
Treatment:
- Rest. Avoid weight-bearing activities as much as possible when your knee is painful and swollen.
- Ice and elevation. Cold therapy can help control pain and swelling. Apply ice to your knee for 15 to 20 minutes every two to four hours. You may use a bag of ice, frozen vegetables or an iced towel cooled down in your freezer. When you ice your knee, raise your knee higher than the level of your heart, using pillows for comfort.
- Pain medication. Over-the-counter drugs such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others) may help relieve your knee pain. If you need something stronger, ask your doctor about prescription medications.
- An ace bandage or velcro knee brace may help
- A needle aspiration may be performed to remove excess fluid.
Breaks and tears will usually require surgery.
See also What is Knee Replacement | ThirdAge
Ligament Injuries:
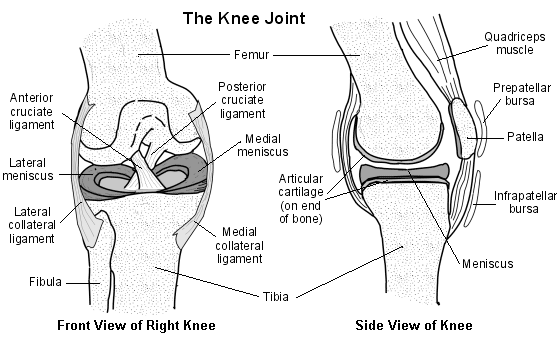
Source: Knee Cartilage Injuries | Patient.co.uk
There are four ligaments in the knee that are prone to injury:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the two major ligaments in the knee. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) in the knee. ACL injuries are a common cause of disability in the knee. In the U.S., 95,000 people get them every year. They are more common in women than men.
Female athletes have four to 10 times more ACL injuries than male athletes have.
See
ACL Injuries in Women
- The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the second major ligament in the knee connecting the thigh bone to the shin bone in the knee.
- The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) connects the thigh bone to the fibula, the smaller bone of the lower leg on the lateral or outer side of the knee.
- The medial collateral ligament (MCL) also connects the thigh bone to the shin bone on the medial or in side of the knee.
See Knee Ligament Injuries: ACL, PCL, and More | WebMD.
|
Meniscus Tear
People can suffer tears of the meniscus because of trauma, sports injuries or the meniscus can tear simply because it wore out. By far, the most common location for a tear is in the back, and on the inner or medial side of the knee -- that is the area we call the posterior horn of the medial meniscus.
Meniscus tears occur 2.5 times more frequently in males than females (Baker), although disorders of the lateral meniscus occur more often in women. The peak incidence of meniscus tears is 31 to 40 years of age in males and 11 to 20 years in females (Baker). A second peak of meniscus tears caused by age-related degeneration occurs in people over age 60. (Levy).
After the initial inflammation subsides, exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstring muscles of the upper leg are usually prescribed.
Conservative therapy with muscle strengthening is frequently all that is needed for minor tears in which good knee function returns as inflammation subsides.
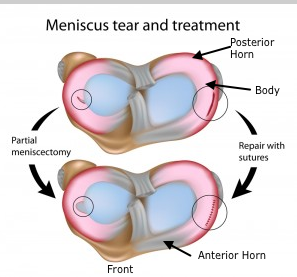 The meniscus has very little blood flow, and it often does not heal. Some patients getting conservative therapy for an old tear may have an occasional knee problem and may eventually choose to have surgical treatment.
The meniscus has very little blood flow, and it often does not heal. Some patients getting conservative therapy for an old tear may have an occasional knee problem and may eventually choose to have surgical treatment.
Candidates for early surgery are patients who have persistent difficulty after the initial inflammation subsides.
Source: Will my meniscus tear heal without surgery? - The Chart - CNN.com Blogs
For those of you who may require surgery, you are concerned about whether or not the tear is repaired or removed. This is very important. Any meniscus tear which can be sutured, should be. Unfortunately only a few meniscal tears have healing abilities, so we are limited in terms of the number of tears we can actually suture.
Source:
Meniscus Tear Surgery --is it always necessary? - Howard J. Luks, MD
Links:
Water on the knee: Lifestyle and home remedies - MayoClinic.com
Water on the knee: Causes - MayoClinic.com
Knee Ligament Injuries: ACL, PCL, and More | WebMD.
What is Knee Replacement | ThirdAge
Meniscus Disorders, Knee | MDguidelines
The Steadman Clinic Vail, CO | Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery | Steadman Hawkins
Why women have an increased risk of ACL injury | American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
ACL Injuries in Women
ACL Injuries in High School Sports: No Gender Difference Found | MomsTeam
ACL at Ski Injuries
Return to Health
last updated 20 Dec 2012
|

