Under Construction 
Although most car battery ratings in Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), are from 540-880, less is required to just crank the engine and the dead battery will usually still be able to supply 100 or more amps, so the jump start cable only needs to support 85-150 amps..
4 cylinder gasoline engine 160 amps
6 cylinder gasoline 210 amps
8 cylinder gasoline engine 250 amps
4 cylinder diesel engine 350 amps
6 cylinder diesel engine 450 amps
8 cylinder Diesel engine 650 amps
Source: Portable Jump Starter Comparison Chart | CarBatteryHelp.com
Cables:
Jumper cables vary in size from AWG 4 to 8. (You may see #10, but it is not recommended).
If the car you're jumping is only a 4, maybe 6 cylinder "Short and thin" (8 gauge) should work. Anything larger needs "long and thick" (6 gauge or lower).
Cold weather starting can add as much as 60% more starter power draw, while a lead-acid battery can lose more than 50% of itŐs cold cranking amps.
However, cable resistance goes down in colder temperature (about 10% less in 32°F vs 7732°F), but not enough to compensate for the above.
Ohms per 1000 ft.
| AWG | 32°F | 77°F |
| 8 | 0.9203 | 1.018 | <
| 6 | 1.463 | 1.619 |
| 4 | 2.327 | 2.575 |
| 2 | 3.700 | 4.094 |
Cheap wires have cheap clamps, which are a pain-in-the-butt to use as well as they are less likely to stand up to time. Cheap clamps are copper plated. Better clamps will be solid copper, which will transmit electricity much better. After utilizing a plated set a few time, the copper can be worn off down to the steel substrate, which does not transmit the electricity nearly as well, meaning your cables won't work very well.
Jump Start Procedure:
See: Car Talk Jump-Start Instructions
Short version:
Read your owner's manual. Some manufacturers do not allow jumpstarts,
and some have fuses that need to be removed before jump-starting, or
other steps that need to be taken before you can successfully jump-start the car.
- Turn off lights on the dead car.
- Turn ignition off on both cars.
- Put on safety gear (eye protection and gloves).
- Turn of accessories lights, radio, ...
- Connect cables according to the diagram below. *
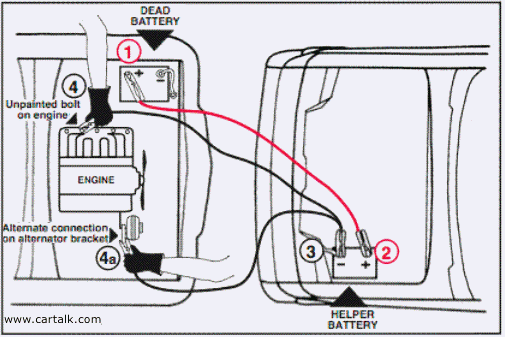
- Start the good car's engine If you have heavy duty cables (AWG 2-6) you can try to start it immediately.
If you have thinner cables wait a minute or two to charge the dead battery. - Revving the engine of the car with the good battery to 2,000 - 2,500 RPM may increase the output of the alternator so it will charge faster.
- Try to start the dead car.
- If the car doesn't start on the first try, shut the supply engine off and disconnect the last connection temporarily while you slightly twist or wiggle each of the four clamps to help ensure a good electrical connection.
- If it still doesn't start let it charge for a little longer, 2-5 minutes.
- When it starts disconnect the cables in the oppisite order from connecting.
- Depending on how dead the battery was and the condition of the battery, you may need to drive it for 5 - 10 minutes at moderate RPM (longer in city driving) so it will start the next time. Many recommend 30 minutes to get it to at least 90% charged or a couple of hours to get it fully charged.
Source: Official Car Talk Jump-Start
Instructions
* Note: Batteries can produce hydrogen and oxygen gas thru electrolysis. In high enough concentrations when exposed to a spark this can produce an explosion.
High concentrations of hydrogen are usually caused by overcharging a battery, but there can be some hydrogen produced during normal operation.
You connect the dead battery last because it is less likely to produce any hydrogen, but you still play it safe by making the last connection, which will produce a spark away from the battery.
Jump Start Batteries:
Links:
Official Car Talk Jump-Start
Instructions
Car Batteries and Batteries in General
How Do I Jump-Start a Car? | LifeHacker.com
Car Talk Jump-Start Instructions
Jump Starting A Car | DrivingTips.org
Wire Size
Return to auto
last updated 11 Jan 2018
|
